Visual Basic is initiated by using the Programs option > Microsoft Visual Basic 6.0 > Visual Basic 6.0. Clicking the Visual Basic icon, we can view a copyright screen enlisting the details of the license holder of the copy of Visual Basic 6.0. Then it opens in to a new screen as shown in figure 1 below, with the interface elements Such as MenuBar, ToolBar, The New Project dialog box. These elements permit the user to buid different types of Visual Basic applications.
The Integrated Development Environment
One of the most significant changes in Visual Basic 6.0 is the Integrated Development Environment (IDE). IDE is a term commonly used in the programming world to describe the interface and environment that we use to create our applications. It is called integrated because we can access virtually all of the development tools that we need from one screen called an interface. The IDE is also commonly referred to as the design environment, or the program.
Tha Visual Basic IDE is made up of a number of components
- Menu Bar
- Tool Bar
- Project Explorer
- Properties window
- Form Layout Window
- Toolbox
- Form Designer
- Object Browser
In previous versions of Visual Basic, the IDE was designed as a Single Document Interface (SDI). In a Single Document Interface, each window is a free-floating window that is contained within a main window and can move anywhere on the screen as long as Visual Basic is the current application. But, in Visual Basic 6.0, the IDE is in a Multiple Document Interface (MDI) format. In this format, the windows associated with the project will stay within a single container known as the parent. Code and form-based windows will stay within the main container form.
picture : the visual basic startup dialog box
Before you start to build-up the form, it will make it easier if you change the color of the form. Otherwise you will be working with grey controls on a grey background. To change the color, just click anywhere on the form, go to the properties window, find the property called BackColor and change it to the standard Window background (teal) or to any color you want in the palette.
In our first example we will need 6 labels and 2 command buttons. Each one of these objects that you put on a Form is called a control. To get a control you go to the Toolbox, click on the control you want, come back to the Form and click and drag the control to the size and position you want. Position the controls somewhat like in the diagram below.
picture : visual basic form
Menu Bar
This Menu Bar displays the commands that are required to build an application. The main menu items have sub menu items that can be chosen when needed. The toolbars in the menu bar provide quick access to the commonly used commands and a button in the toolbar is clicked once to carry out the action represented by it.
Toolbox
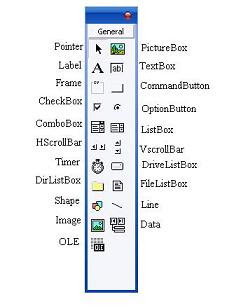
The Toolbox contains a set of controls that are used to place on a Form at design time thereby creating the user interface area. Additional controls can be included in the toolbox by using the Components menu item on the Project menu. A Toolbox is represented in figure shown below.
picture : Toolbox window with its controls available commonly
- Pointer Provides a way to move and resize the controls form
- PictureBox Displays icons/bitmaps and metafiles.
- TextBox Used to display message and enter text.
- Frame Serves as a visual and functional container for controls
- CommandButton Used to carry out the specified action when the user chooses it.
- CheckBox Displays a True/False or Yes/No option.
- OptionButton control which is a part of an option group allows the user to select only one option even it displays mulitiple choices.
- ListBox Displays a list of items from which a user can select one.
- ComboBox Contains a TextBox and a ListBox. This allows the user to select an ietm from the dropdown ListBox, or to type in a selection in the TextBox.
- HScrollBar and VScrollBar These controls allow the user to select a value within the specified range of values
- Timer Executes the timer events at specified intervals of time
- DriveListBox Displays the valid disk drives and allows the user to select one of them.
- DirListBox Allows the user to select the directories and paths, which are displayed.
- FileListBox Displays a set of files from which a user can select the desired one.
- Shape Used to add shape (rectangle, square or circle) to a Form
- Line Used to draw straight line to the Form
- Image used to display images such as icons, bitmaps and metafiles. But less capability than the PictureBox
- Data Enables the use to connect to an existing database and display information from it.
- OLE Used to link or embed an object, display and manipulate data from other windows based applications.
- Label Displays a text that the user cannot modify or interact with.
- - - Next